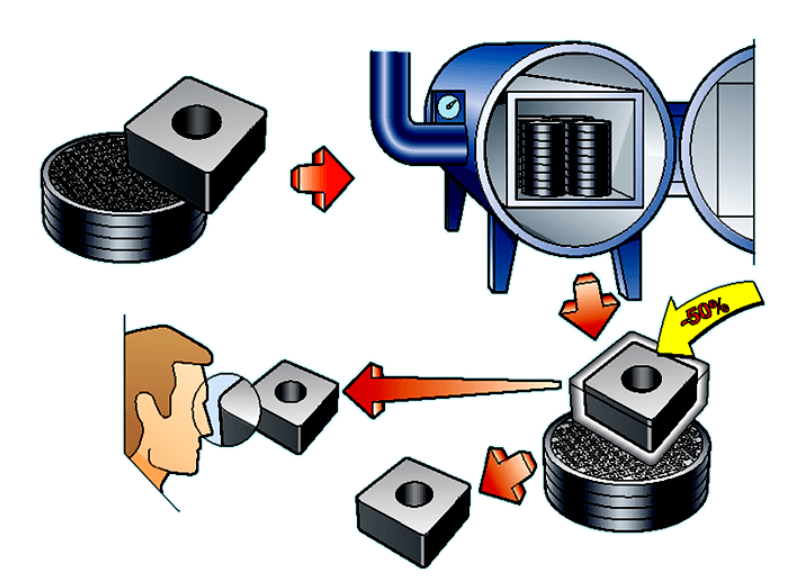
Cemented carbide is a powder metallurgical product made from carbide (wc, tic) micron-sized powder of high hardness refractory metals with cobalt (co) or nickel (ni) and molybdenum (mo) as the binder, sintered in a vacuum furnace or hydrogen reduction furnace.
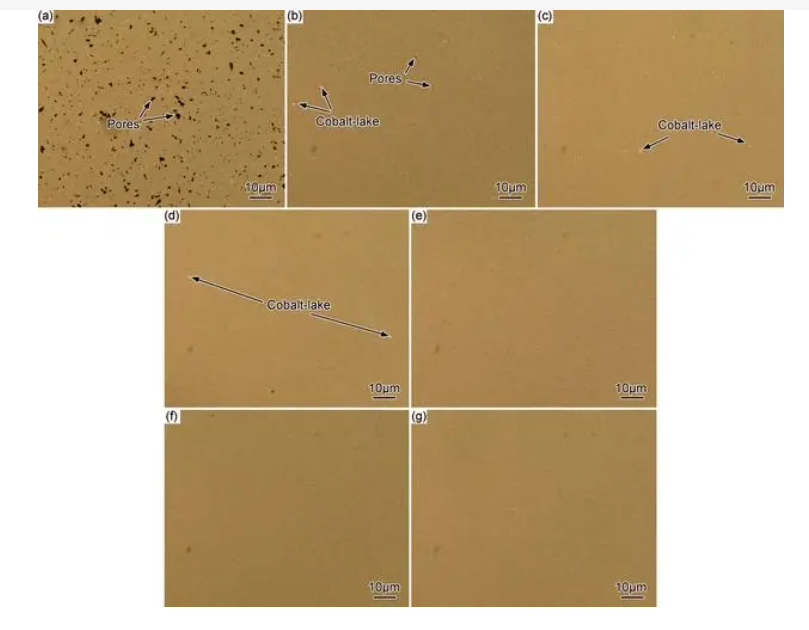
When manufacturing cemented carbide, the size of the raw material powder chosen is between 1 and 2 microns, and the purity is very high. The raw materials are dosed in the prescribed proportion, added to alcohol or other media in a wet ball mill, so that they are fully mixed, crushed, dried, sieved and added to wax or gum and other types of molding agents, and then dried and sieved to make a mixture. Then, the mixture is granulated, pressed, and heated to near the melting point of the bonded metal (1300 ~ 1500 ℃), the hardened phase and the bonded metal will form a eutectic alloy.
After cooling, the hardened phases are distributed in a grid composed of bonded metals, which are closely linked to each other to form a solid whole. The hardness of cemented carbide depends on the hardening phase content and grain size, i.e. the higher the hardening phase content and the finer the grain size, the greater the hardness. The toughness of cemented carbide is determined by the bonding metal, and the higher the bonding metal content, the greater the bending strength.
Post time: Jun-09-2023