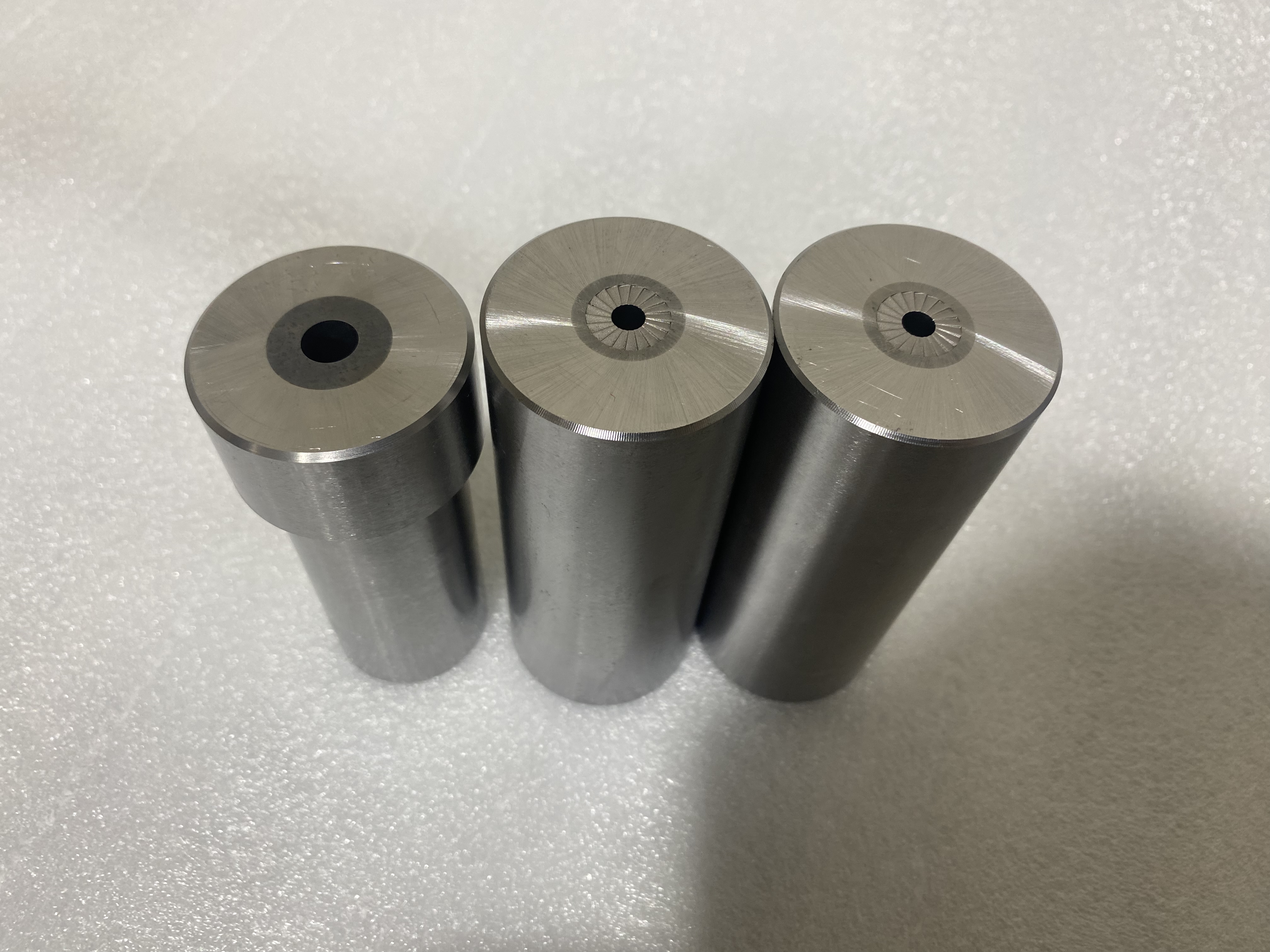
Cemented carbide is a composite material produced by powder metallurgy from a refractory metal hard compound and a bonding metal or alloy; it is a cermet. Refractory metal hard compounds usually refer to carbides, nitrides, borides and silicides of transition elements (tungsten, titanium, vanadium, molybdenum, zirconium, hafnium) in groups IV, V and VI of the periodic table. things. Widely used in cemented carbide are carbide, titanium carbide, tantalum carbide and niobium carbide. The common characteristics of these carbides are: high melting point, high hardness, good chemical stability, and good thermal stability. The best bonding metal is cobalt, followed by nickel and iron. Carbide has the following advantages and characteristics:

(1) High hardness, high wear resistance and high high temperature hardness. The room temperature hardness of cemented carbide can reach HRA94, the high temperature hardness exceeds the room temperature hardness of high speed steel at 600°C, and exceeds the room temperature hardness of carbon steel at 1000°C.
(2) High elastic modulus, usually 390~690GPa. (3) High compressive strength, up to 6GPa.
(4) Some cemented carbide has good chemical stability. It is acid and alkali resistant and does not undergo significant oxidation even at 600~800°C.
(5) Small thermal expansion coefficient; thermal conductivity is close to that of iron and its alloys. (6) Impact toughness is relatively low.
Post time: Jan-01-2024