The sintering of cemented carbide is liquid phase sintering, that is, it is carried out under the condition that the bonding phase is in liquid phase. The compact is heated to 1350C-1600C in a vacuum furnace. The linear shrinkage of the compact during sintering is about 18%, and the volume shrinkage is about 50%. The exact shrinkage depends on the particle size of the tungsten carbide powder and the composition of the cemented carbide.

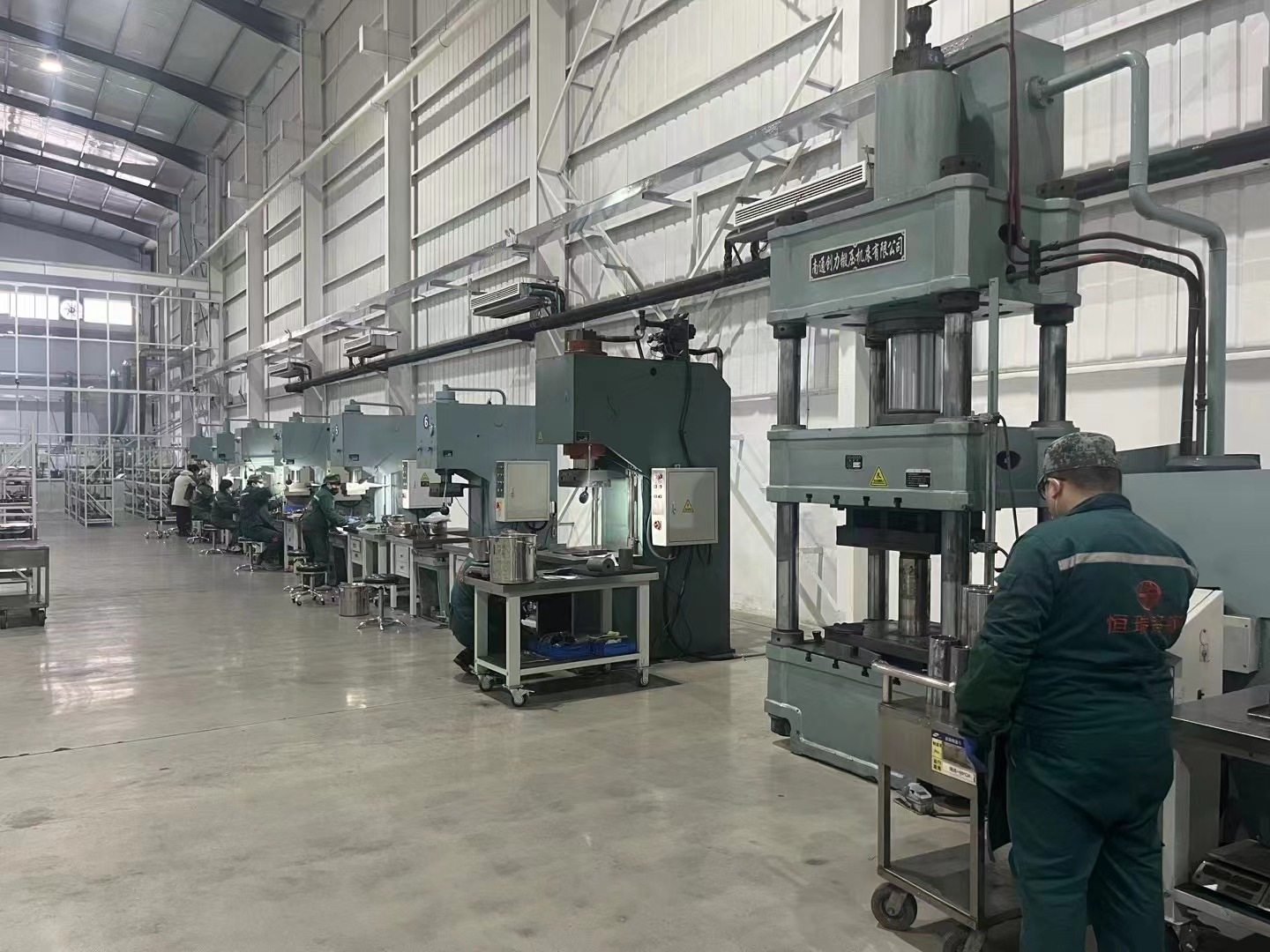
The sintering of cemented carbide is a complex physical and chemical process, which includes plasticizer removal, degassing, solid phase sintering, liquid phase sintering, alloying, densification, dissolution and precipitation, etc. The compact forms products with certain chemical composition, organizational structure, performance and shape and size under specific sintering conditions. These process conditions vary greatly depending on different sintering devices.

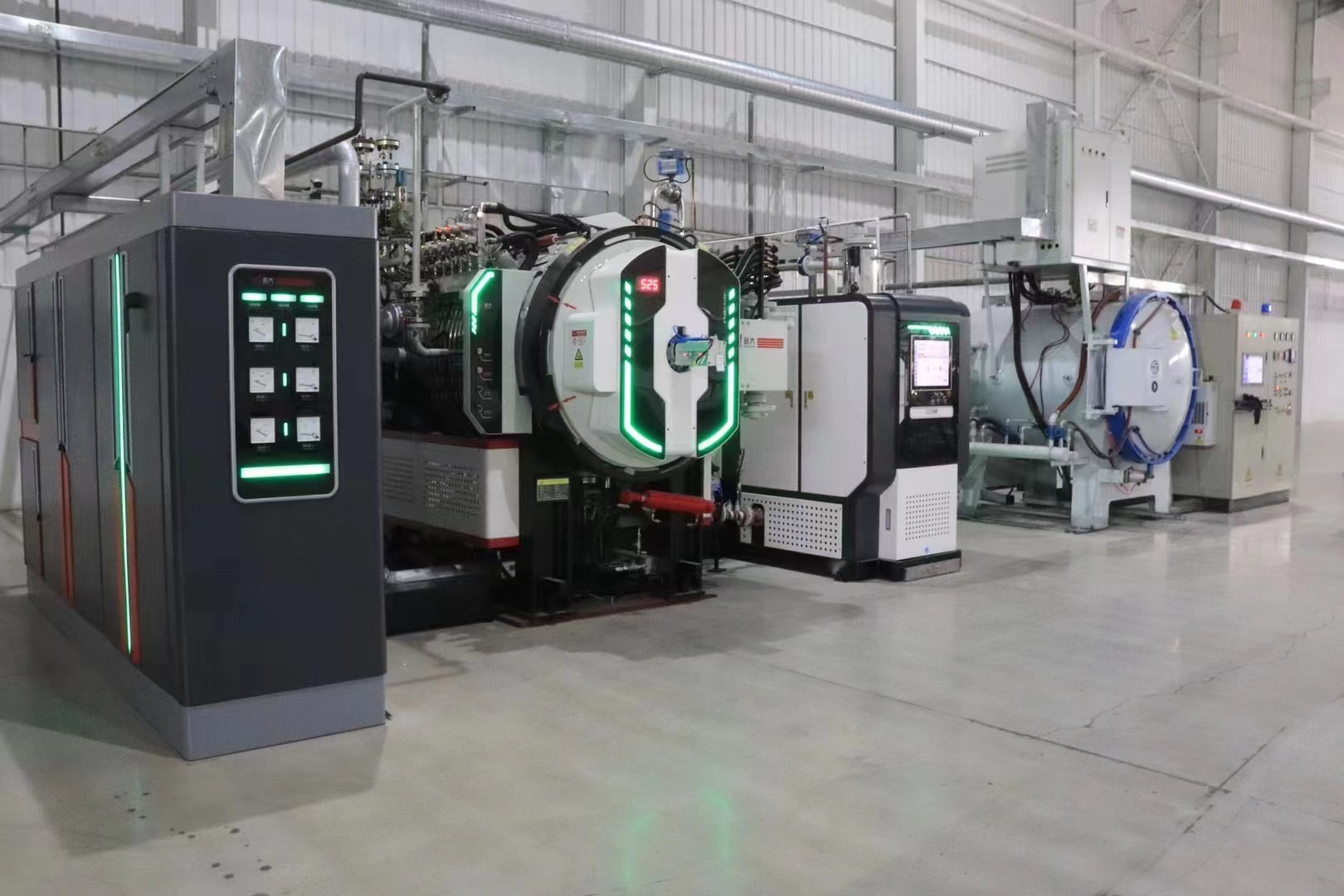
Carbide vacuum sintering is a process of sintering at less than 1atm (1atm=101325Pa). Sintering under vacuum conditions greatly reduces the hindrance of densification by adsorbed gas on the powder surface and gas in closed pores, which is conducive to the diffusion process and densification, and avoids the reaction between metal and certain elements in the atmosphere during the sintering process. It can significantly improve the wettability of the liquid bonding phase and the hard phase, but care should be taken to prevent the evaporation loss of cobalt during vacuum sintering. Vacuum sintering can generally be divided into four stages, namely plasticizer removal stage, pre-sintering stage, tungsten carbide high-temperature sintering stage, and cooling stage.
Post time: Feb-22-2024